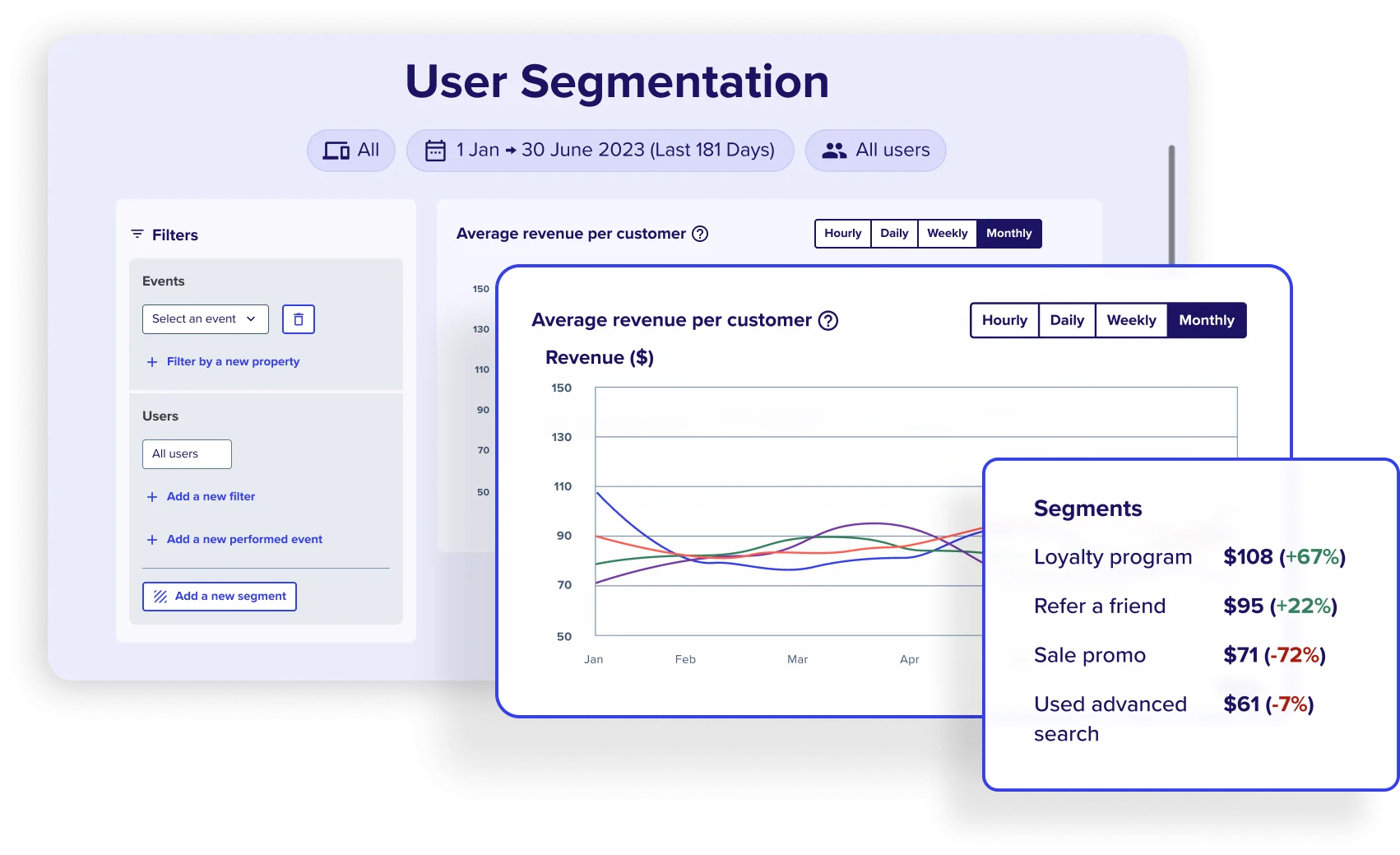
Use Contentsquare to understand how different users behave
Create meaningful customer segments to get fast, relevant insights about your most important users with Contentsquare.

When you’re building, marketing or optimizing a product, there’s no ‘one size fits all’. No two customers have the same exact needs—so how do you address them?
The answer is to put your product users into useful categories—otherwise known as customer segmentation.
By dividing your customers into groups with similar attributes—from who they are to how they use your website or product—you find ways to address each segment’s needs, preferences and pain points.
This guide covers everything you need to understand your user base and deliver a customer experience (CX) every one of your customers loves, seeks and deserves.
Customer segmentation is the process of sorting customers into different groups based on their shared characteristics—like preferences, behavior or demographics. This helps you understand your customers better and serve them in a way that feels more personal and tailored to their needs.
Basically, segmentation is like sorting through your customer base to find out what they have in common—what they do, what they need and what they like. Then, with the results from your customer segmentation analysis, you can tailor marketing efforts and campaigns, sales outreach and product messaging to each of these different customer groups.
This simple act of spotting similarities or patterns is a game-changer for your company, boosting empathy, retention and loyalty, while giving your customers exactly what they want.
Terms like ‘customer’ and ‘user’ may sound similar, but they differ in context: customers make purchases, while users engage with products or services.
For segmentation, both methods involve grouping individuals by their traits or actions, with each applied differently in marketing and product development:
Use Contentsquare to understand how different users behave
Create meaningful customer segments to get fast, relevant insights about your most important users with Contentsquare.
Different ways or models of segmenting customers let you understand, empathize with and meet the needs of various groups of individuals who share similar characteristics.
Here are nine different customer segmentation types and how to use each one to build more meaningful, relevant experiences:
Exploring segmentation modelsThis is by no means an exhaustive list of segmentation models. There are a number of other different types for you to explore. For example, here’s how Ellie Wheeler, Senior Product Analyst at Hotjar, part of the Contentsquare group, uses recency, frequency, and monetary value (RFM) segmentation to evaluate customer behavior:
“RFM segmentation can provide valuable insights into customer behavior and their engagement. We use it to tailor the product experience to the specific needs and lifecycle points of customers.
“This method is especially helpful in segmenting customers to identify the highest performing across the three metrics (Recency, Frequency, Monetary) and understanding the steps these users took. We use those insights to increase product adoption and engagement by guiding customers to be more like these top performers.”
Customer segmentation isn’t just a tool for analysts—it benefits everyone from product managers to marketers. Take a look at how each team leverages their own customer segmentation strategy and the results it leads them to:

To get a sense of how this simple sorting process can be used to fine-tune your CX approach, check out these three customer segmentation benefits. Don’t forget to tune into our dedicated chapter to learn how to perform customer segmentation and see more use cases.
Segmentation is great for developing an accurate picture of your ideal customers, AKA buyer personas. Building buyer personas reveals the different ways people search for, buy and use your site or product—helping you focus and prioritize your efforts, design better marketing messages and improve retention.
Start by talking to customers to create personas based on your existing user base:
Then, divide these personas further into segments to improve your understanding:
Once you’ve observed common characteristics among your segments, you can tailor their experiences strategically and deliver features or solutions that meet people’s needs in their specific context.
For example, you could
How New Balance personalized customer experiences with Contentsquare
Jessica Bartlett, CRM Manager EMEA at New Balance, champions personalization in eCommerce. She knew that to truly personalize user experiences, she needed to dive deep into the nuances of customer behavior. By analyzing and leveraging existing customer data, Jessica crafted segments based on shopping habits and preferences.
“Like visitors who have viewed your products within a certain amount of time,” she explained, “or visitors that have looked at specific product pages or styles.”
Understanding her target customers’ journey was key. Insights from Contentsquare transformed these narratives into personalized experiences that resonated deeply with New Balance’s audience.
While your products or services alone deliver value to your users, it’s your CX—the culmination of all interactions a customer experiences with your brand over time—that truly sets you apart.
Throughout the customer segmentation process, you create personalized moments and give each group the attention they deserve, increasing customer lifetime value (CLV) and customer loyalty and turning them into your biggest fans.
Say you’re puzzled about why your product’s casual users aren’t upgrading or renewing their subscription plan or why your newest customers are hitting a roadblock at onboarding. This type of segmentation streamlines the process of understanding exactly what’s going on with valuable customers, and what you can do about it. And it goes like this:
With this personalized approach to user analytics, you get answers to specific questions about your audience and use those insights to improve CX with segmentation.
When done right, customer segmentation teaches you more about your most valuable cohorts of users, giving you deep insights into the audiences that matter most.
You may find these segments helpful for an effective digital experience strategy:
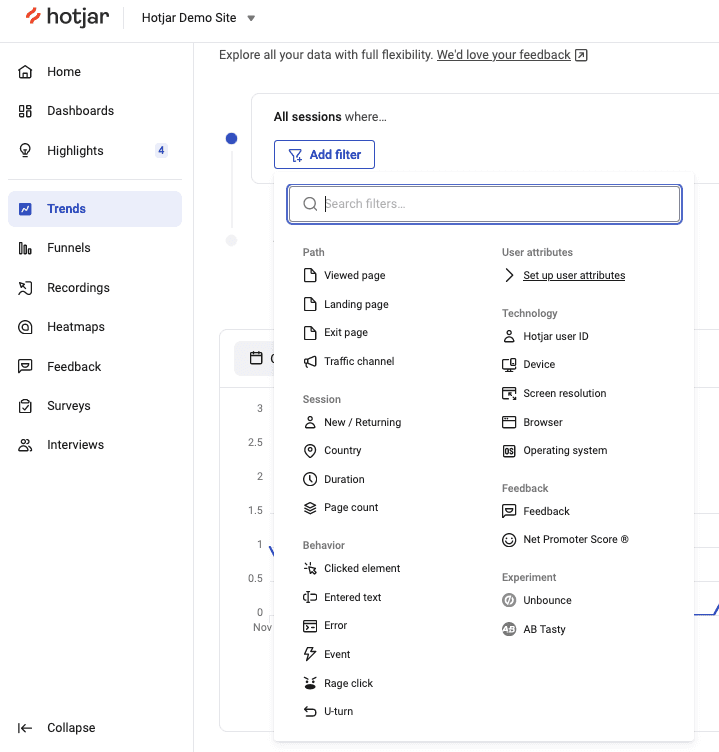
🔥 If you’re using Hotjar: All Hotjar tools include filters that let you drill down into your data and find valuable information. Use these to apply different types of market segmentation, for example:
Your business is already collecting user data, but there’s a chance you’re not leveraging it to its fullest extent. By segmenting customers, you unlock the potential of your data—so you can put your learnings into action to optimize your digital experience and drive growth.
Keep reading for deeper insights into what delights and frustrates every segment of your digital customers:

Take a product tour
Get to grips with Contentsquare fundamentals with this 6 minute product tour.
Segmentation models come in a variety of attributes and characteristics. The four most common are
The number of segments you use depends on your customer data, products and prioritization capabilities. For instance, a SaaS start-up may be able to handle three to five segments, while more enterprise solutions could manage six to eight at a time.
Customer segmentation enhances CX by allowing you to provide your users with personalized, precise messaging and relevant features and solutions. This approach helps you improve user satisfaction, get higher retention rates and create more effective product iterations based on segment-specific feedback.