Not all your customers want the same thing. But when you categorize them using different customer segmentation models, you start noticing similarities within each segment.
These models let you tailor your marketing efforts and create products for smaller user groups. Catering to your customers’ specific characteristics makes them more responsive to your messaging or offering. This give-and-take dynamic enhances product development, user engagement and customer satisfaction.
This article covers the different types of customer segmentation models, helping you gain deeper insights into your customer base and create digital experiences and marketing campaigns that your priority segments will love.
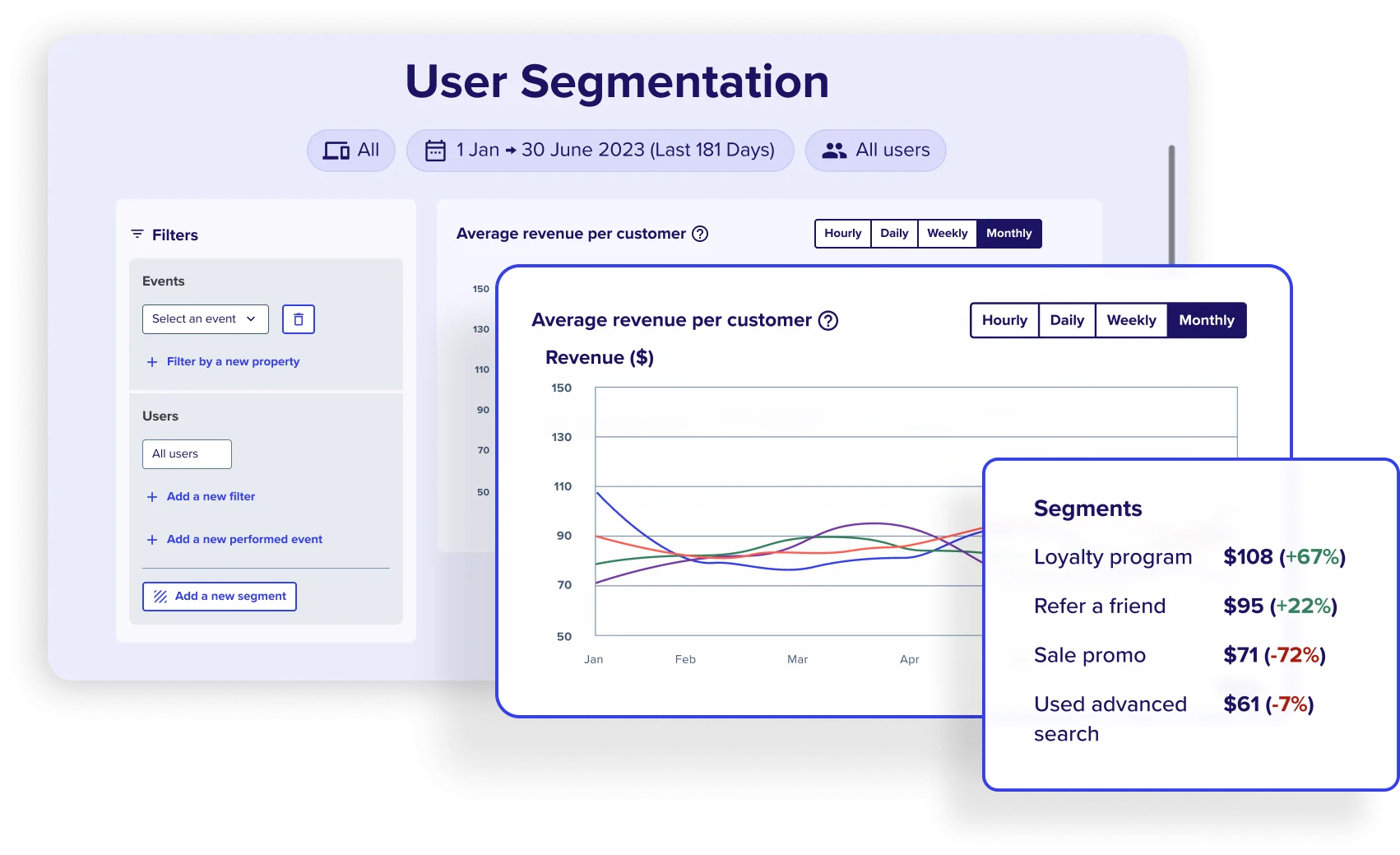
Use Contentsquare to understand how different users behave
Create meaningful customer segments to get fast, relevant insights about your most important users with Contentsquare.
1: Demographic segmentation
Demographic segmentation groups people based on their individual attributes such as age, gender, education, income, occupation, family size, marital status, race and religion.
Why use it: This approach categorizes your customer base using accessible labels, leading you to make faster decisions. For example, if your solutions attract high-income earners, your next move would be to adapt your pricing and packages. Do you see a high number of users from Spain? Then, including Spanish in your list of translated languages is a given.
What to watch out for:Demographic data may be too vague to help you understand what users truly need and want. It may also lead you to generalize some user groups, e.g. millennials are entitled, or women are less interested in coding.
How to collect demographic data: Look for existing information in your database, e.g. from sign-up forms and demo requests. Gather historical data from site analytics platforms like Google Analytics or product analytics platforms like Contentsquare.
Surveys are another great way to gather demographic customer data. Use tools like Hotjar, part of the Contentsquare group, to launch a product feedback or exit-intent survey. Add demographic questions at the end and allow respondents to opt out of answering sensitive questions about age, gender, race or religion.
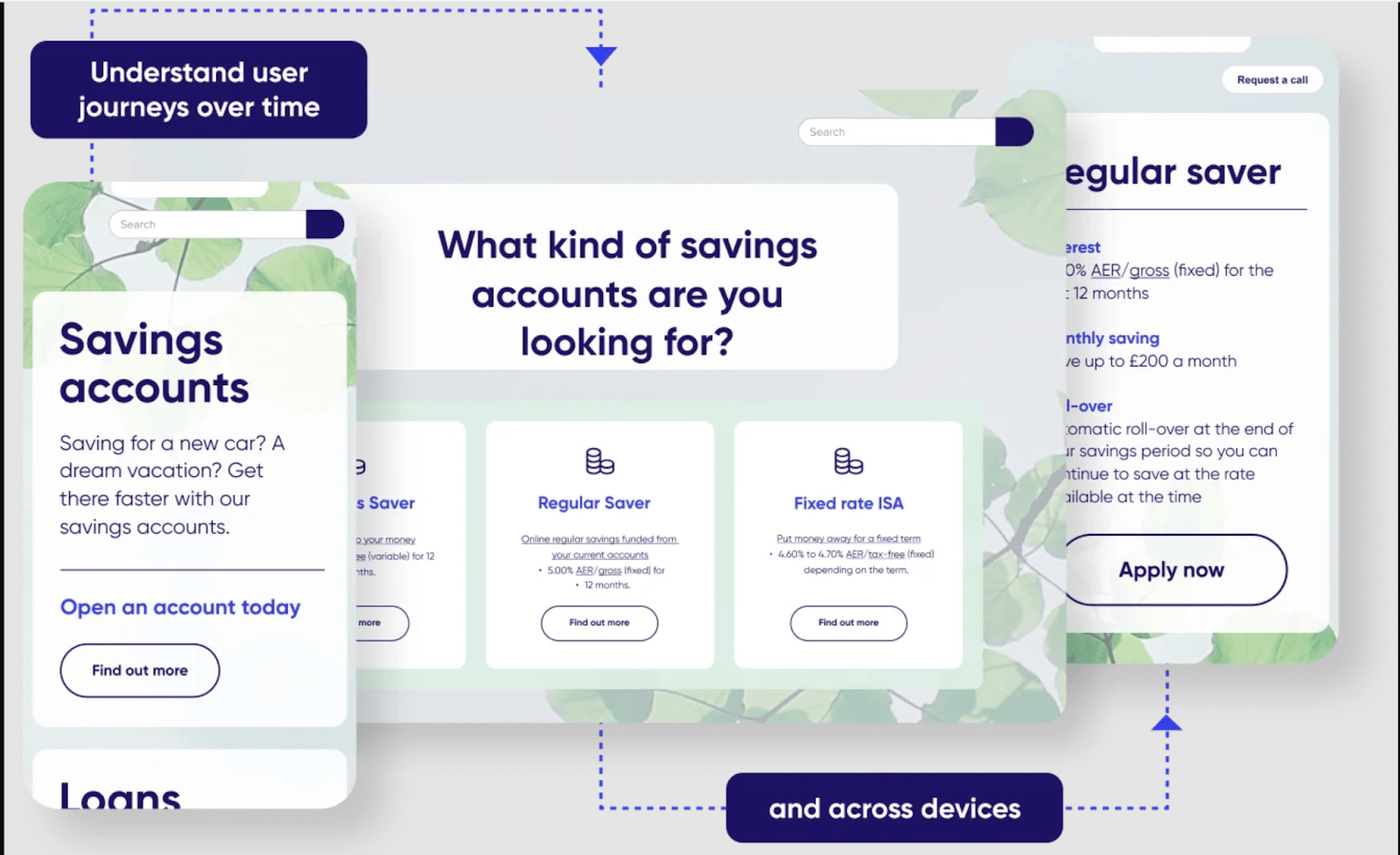
Go beyond segmenting your customers and gain insights into how they behave on your product or website—only with Contentsquare
2. Geographic segmentation
Geographic segmentation, a subset of demographic segmentation, sorts customers based on their location—including city, country or region. You can also focus on climate, language, population and culture to uncover trends and patterns.
Why use it: Geographic segmentation shows you your customers’ prevalent habits, needs and preferences by area. The resulting data helps you refine your targeting and marketing efforts, and improve customer satisfaction. Think about how people from one region take advantage of your product’s multiple features while those from another prefer a simplified user interface.
What to watch out for: While the geographic approach adds another layer to customer profiles, you need to combine it with other models to get more accurate targeting.
How to collect geographic data: Primary data can come from your website, social media and sales. You can also tap into customer analytics platforms like Hotjar. Set up AI-powered surveys, powered by Hotjar, to ask a random sample of your customer base about their product preferences. Analyze their responses by region for geographic insights.
3. Behavioral segmentation
Behavioral segmentation tells you how users perceive, become aware of, buy and use your brand, product or service. These customer behaviors evolve depending on various factors, such as consumer trends, technology and the economy.
Why use it: This model uses historical behavior patterns to predict future decisions. You can tailor past insights to new content and offerings to create a delightful customer experience. By keeping specific groups happy, such as power users, you inspire customer loyalty, increase lifetime value, boost retention and prevent churn.
What to watch out for: Behavioral segmentation relies on qualitative data—so it deals with certain assumptions for forecasting. To avoid errors, your team must have the technical expertise and resources to group customers effectively.
How to collect behavioral data: Avoid manually collecting behavioral data. Instead, assess customer performance across multiple sessions with Contentsquare’s User Segments tool that lets you analyze and sort customers with similar cross-channel journeys. You can then use these insights to improve your digital experience and the customer journey, optimizing self-serve and reducing the need for live support.
4. Psychographic segmentation
This segmentation model delves into the inner workings behind customer actions and decisions. If behavioral segmentation tells us the what, psychographic segmentation offers the why. It divides customers based on psychological criteria like hobbies, interests, core values, lifestyle and social status.
Why use it: Psychographic segmentation data helps you understand the nuances of customer pain points and desires, painting the big picture that enables you to position your product better. For example, some fitness apps cater to one customer group that cares about getting enough exercise and another that prioritizes quality sleep.
What to watch out for: Compared to the other three main types of customer segmentation above, psychographic segmentation is more complex. It requires quantitative and qualitative research, and well-defined standards for interpretation.
How to collect psychographic data: Busy product teams can rely on Engage, powered by Hotjar, to automate user research. Use Engage to screen participants, and schedule, host and document moderated interviews on your behalf. Then launch another Hotjar survey to validate your results.
5. Firmographic segmentation
Firmographic segmentation is the counterpart of demographic segmentation—but for businesses. It focuses on attributes like a company’s industry, size, number of employees and location. Business-to-business (B2B) companies use it to understand the buying preferences of small and mid-sized firms and enterprises.
Why use it: This customer segmentation model enhances customer targeting, engagement and retention. Segmenting your B2B customers by industry lets you tailor your messaging based on your target industries’ distinct language and pain points. Personalization makes audiences more receptive and increases the chance that they’ll do business with you again.
What to watch out for: Criteria like industry can be too broad. Complement the firmographic method with other customer segmentation models to create more actionable strategies. For example, combine firmographics with behavioral segmentation to understand how clients interact with your product, or integrate psychographic segmentation to gain insights into your customers’ values.
How to collect firmographics data: Gather updated data from public listings, government records, company websites and fee-based databases. You can also build out your B2B customer profiles by conducting surveys with existing customers. For example, use a Net Promoter Score® (NPS®) survey to learn what drives businesses to come back.
6. Technographic segmentation
This approach groups your customers based on the technology they use to access your site or product. Technographic variables include device type (e.g. mobile, tablet or laptop), software (e.g. operating systems) and other factors like the use of artificial intelligence (AI) tools.
Why use it: Technographic segmentation supports your team’s goal to deliver a delightful digital experience across different devices and ensure your product is responsive. It offers insights into which kinds of technology are broadly used and which ones to design for.
What to watch out for: Technology adoption rates change rapidly. As such, your segments can quickly become outdated. They may no longer reflect today’s conditions, especially if they were created over three years ago.
How to collect technographic data: You can collect data through web scraping and third-party sources. Tap into Mobile Analytics, powered by Heap, part of the Contentsquare group, to glean insights into how your customers continue their journey from web to mobile, and vice-versa. And last but not least, Contentsquare’s Product Analytics tools come in handy in tracking end-to-end user journeys, including the technology deployed throughout.
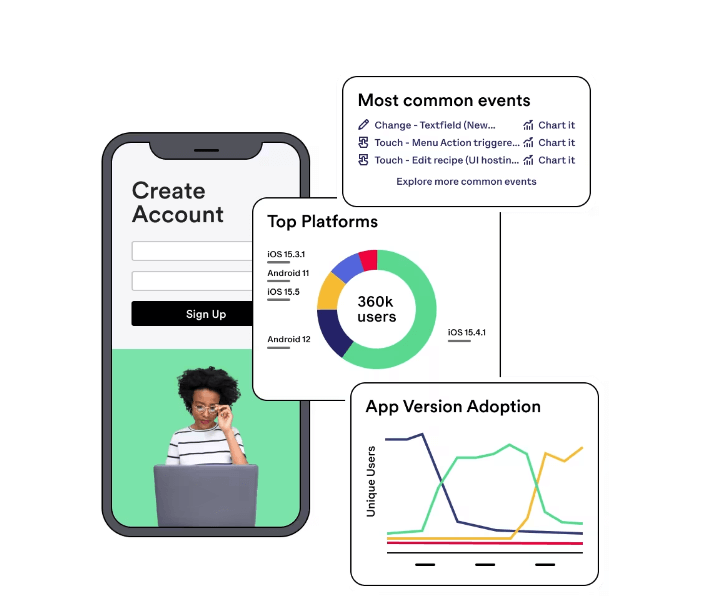
Use mobile analytics to capture your customers’ web and mobile data.
7. Needs-based segmentation
Needs-based segmentation categorizes customers according to their shared needs, challenges and pain points.
Why use it: This segmentation model allows you to recognize unmet customer needs. Imagine a segment of event organizers: they might need a unified system for event scheduling, attendee management, engagement tracking and data analytics. It also helps you identify if this need is common among multiple segments and prioritize the improvements with the biggest business impact.
What to watch out for: Needs-based segmentation involves collecting qualitative data through surveys, interviews, session recordings and heatmaps. However, these insights won’t be entirely useful without measurable data like customer satisfaction scores and engagement metrics to pinpoint your target audience’s most important problems and desires.
How to collect needs-based data: Combine insights—from tools like session recording and heatmaps—that allow you to observe your customers on your product or website with data from sales, web analytics and social media. Filter your segments on Hotjar and find the most relevant session recordings to get a firsthand view of their full journey.
8. Value-based segmentation
This type of segmentation divides customers based on the revenue they bring to your business. It also factors in the cost required to build and maintain a relationship with them. This way, you can tell which segments are the most and least profitable and optimize your marketing strategies to target customers effectively.
Why use it: Value-based segmentation enables you to allocate resources to the right projects and initiatives. For example, if you discover that enterprises make up your high-value segment, your sales and marketing teams can then focus their efforts on acquiring and retaining enterprise clients.
What to watch out for: As with the other customer segmentation models, value-based segmentation may overlook the diversity among individuals making up a segment. It also ignores the non-monetary value that customers bring to your business. Therefore, it’s important to consider variables such as brand advocates who influence other people’s purchases despite not being a part of the high-value group.
How to collect value-based data: Tap into your customers’ transactional history, e.g. purchase size and purchase frequency, and indirect data from customer relationship management (CRM) platforms (like chat logs and conversion probability). Complement this data with insights from retention analytics, like engagement across your customer touchpoints, particularly those with the most impact on conversions.
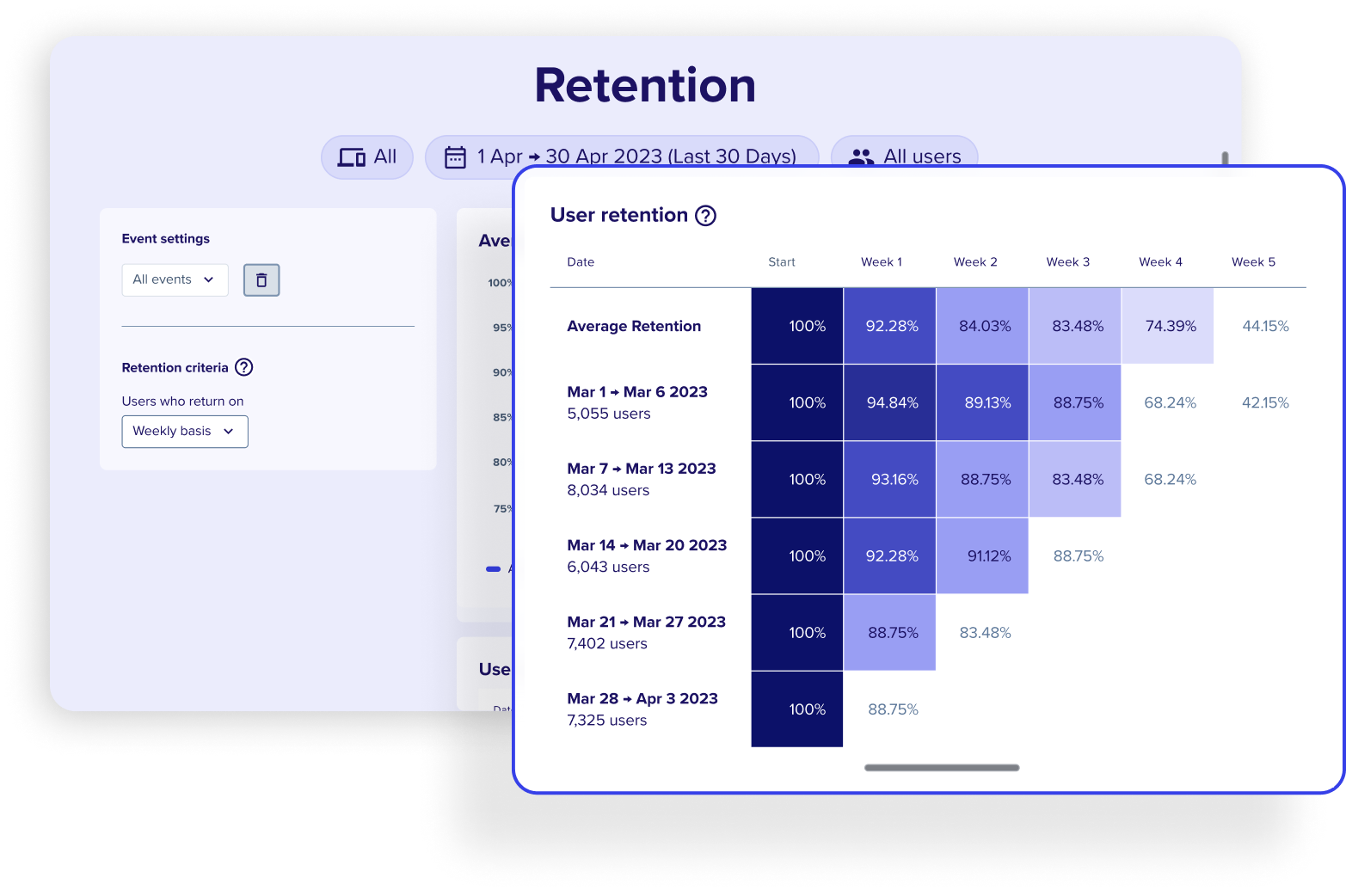
Use Contentsquare’s Retention Analysis, powered by Heap, to uncover the journey your high-value customers took to reach conversion
Combine your segmentation models to refine targeting
Depending on your business goals, combine different models to create a more accurate picture of your segments. Align various data points from these models to refine your customer segmentation analysis and achieve greater accuracy. It’s an effective way to reach out to the right customers at the right time.
For example, if you have a diverse customer base, use demographic, geographic and behavioral segmentation to get the smallest variations among customers within each segment.
Instead of focusing solely on revenue, consider the behavior behind a purchase, particularly how recent and frequent it is. This blended approach allows you to categorize high-level, loyal customers and occasional buyers.
FAQs about customer segmentation models
What is customer segmentation?
Customer segmentation is a process that divides a customer base into distinct groups that share similar characteristics. It allows product teams to tailor their product development and strategies to the specific needs and preferences of each group. These targeted efforts then lead to more effective customer engagement and improved business outcomes.
What are the benefits of customer segmentation?
The benefits of customer segmentation include enhanced targeting and personalization, which can lead to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty. By understanding the unique needs and behaviors of different segments, companies can optimize their resources, improve product and service offerings, and achieve better market penetration. Additionally, segmentation helps in identifying new opportunities for growth and innovation within specific customer groups.
What are customer segmentation models?
Customer segmentation techniques or models refer to the distinct ways of dividing your customer base into groups according to shared characteristics.
The main types of customer segmentation are
- Demographics segmentation
- Geographic segmentation
- Behavioral segmentation
- Psychographic segmentation
- Firmographics segmentation
- Technographic segmentation
- Needs-based segmentation
- Value-based segmentation
