For several years, our team has been sharing best practices and predictions on how to prep your site performance and UX not only for today but also for tomorrow. We aren’t exaggerating when we say that 2021 will be a turning point for user experience.
Especially considering that the most popular search engine in the world will be switching up its search algorithm in May 2021. The name of this update? The Google Page Experience.
In this guide, we offer concrete solutions to help you prepare your site for the arrival of this new update. But first, let's take a look at how the famous search engine works and what the update will change.
A Brief History of Web Research
The goal of a search engine is to provide a user the most relevant answer(s) to their query.
It does this by crawling millions of web pages every day with "crawlers" or "spiders", copying and storing the information collected in a database which then allows these pages to be displayed by the engine.
However, search engines must also order these results so that the most relevant pages are the most accessible to Internet users. Brands typically compete to land in the top 3 search results, or in position 0, to capture the most views and traffic from searchers.
In order to determine a site’s ranking ability, a search engine takes into account a number of "criteria'' that are as varied as they are numerous. Google currently uses more than a hundred different criteria to determine where a site will land on a search results page.
A few examples of Google’s ranking criteria include:
- Content relevance
- Keywords used
- The freshness of information
- And the quality of links and domains that point to a page or a domain
But, just when you think you’ve mastered Google’s algorithm, they go and change it. Google is constantly evolving and updating its algorithm to bring its users the best possible experience and connect them even faster to the content they need.
While most of these updates are minor, some have a visible impact and have left a lasting mark on a website’s SEO and ability to appear in searches.
This was the case in the 2019 Google panda update which targeted low-quality content, the penguin update in 2012 which attacked bogus inbound links, or more recently the Rankbrain algorithm used to better understand the search intent of a user. The latter also marked an important turning point in Google search history, since it (finally) put the Internet user officially at the heart of search engine improvement.
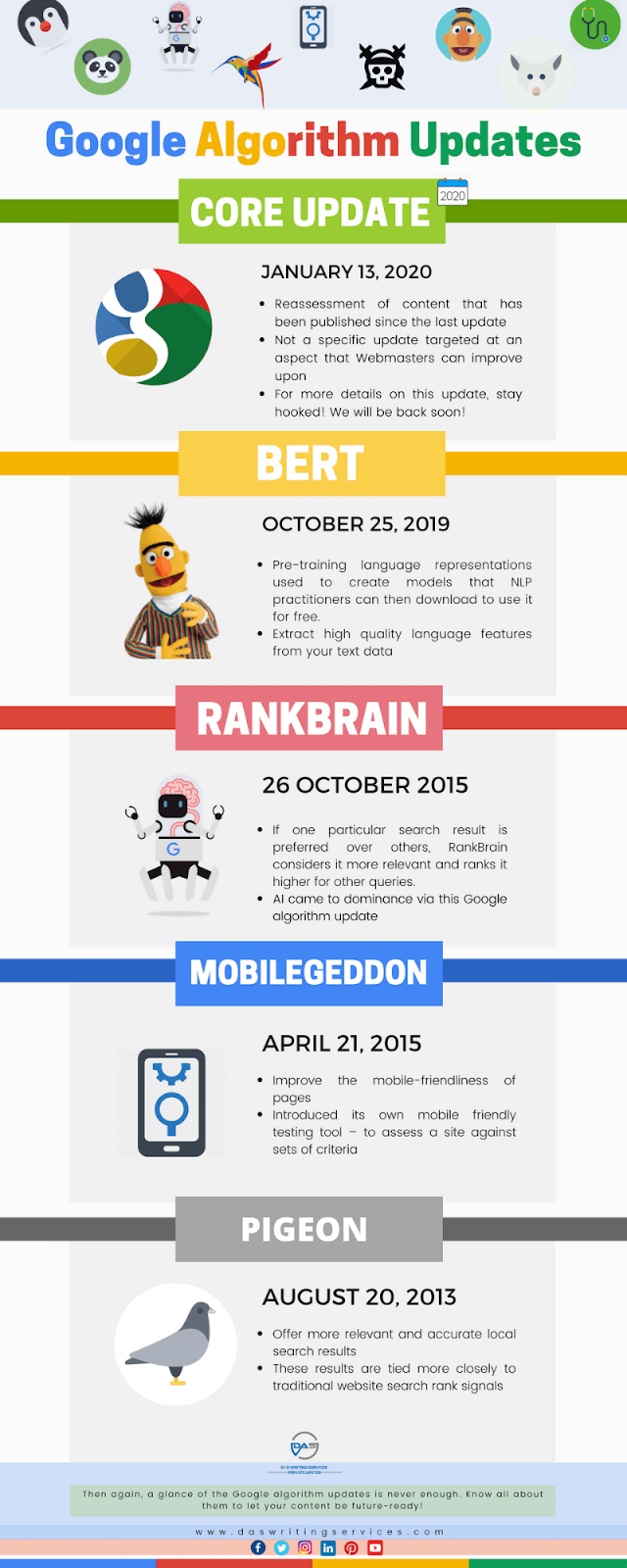
Some examples of major Google algorithm updates - Source: Das Writing Services
Since then, interest in consumer needs and user experience has grown steadily. And the numbers don't lie. According to Contentsquare research, one in two visitors leave a site after only viewing one page! We even found that for every 100 milliseconds a page takes to load, conversion rate drops by 7%.
Search engines can no longer ignore these figures. That’s why they’re slowly but surely moving us from the era of SEO to that of SXO.
SXO: What is It?
SXO (Search eXperience Optimization) is the combination of SEO and UX, or user experience.
SXO aims to improve a site’s visibility on search engine results pages by optimizing the on-page experience for users. For acquisition experts, this means looking past traffic performance to now consider conversion data, as well.
After all, being the first search result won’t do you much good if your bounce rate is high. Keep in mind though that every bounce rate benchmark by industry is different.
Search eXperience Optimization is a concrete response to various Google updates in recent years:
- The emergence of universal search in 2007 and the diversification of the content offered on search engine result pages (SERPs), including images, videos, the knowledge graph, and Google News
- The arrival of structured data or rich snippets allowing the display of enriched results for content such as cooking recipes, events, training courses, reviews, FAQs, etc.
- The implementation of featured snippets offering a direct answer to a user's question at the top of the SERP
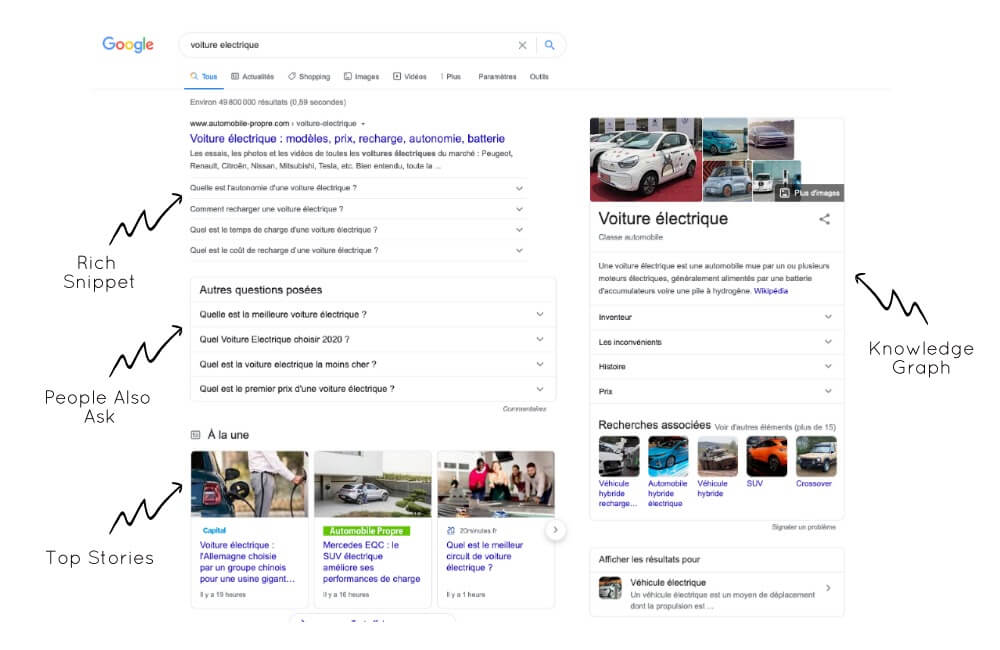
With the Google Page Experience (GPE) update, user experience takes on a whole new dimension as it now becomes a positioning criterion in its own right.
Just like how Panda helped produce better web content and Penguin created healthier linking strategies, we can bet that GPE will popularize UX more widely.
FAQ: The Google Page Experience Update
What is the Google Page Experience Update?
The Google Page Experience update factors in the perceived quality of a web page's user experience to determine its ranking in search engine results.
While this update places a heavier level of importance on specific UX signals, Google has been using UX signals to assess the quality of the UX of a page or site for some time. This includes:
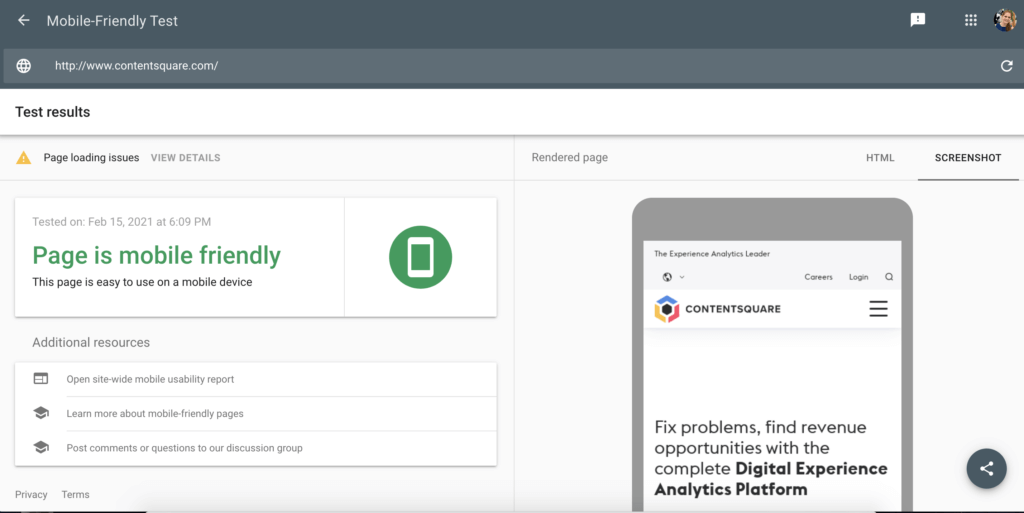
- The mobile-friendliness of the page,
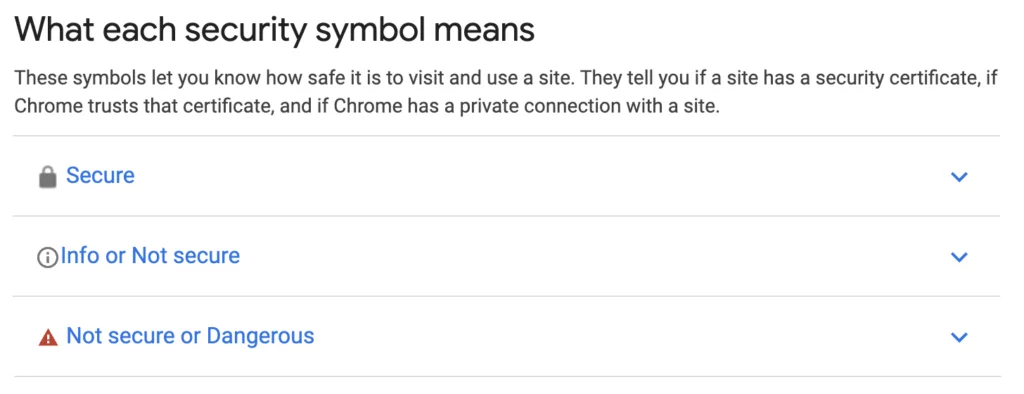
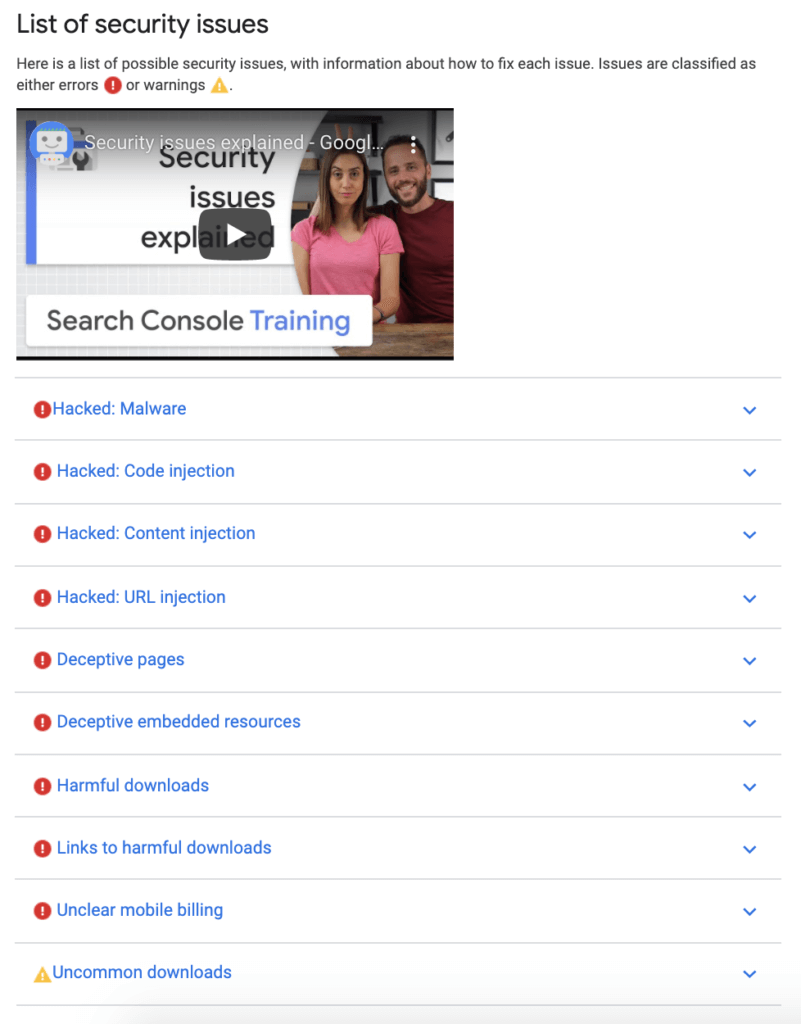
- Secure browsing (malicious or deceptive content on the page),
- The implementation of HTTPS,
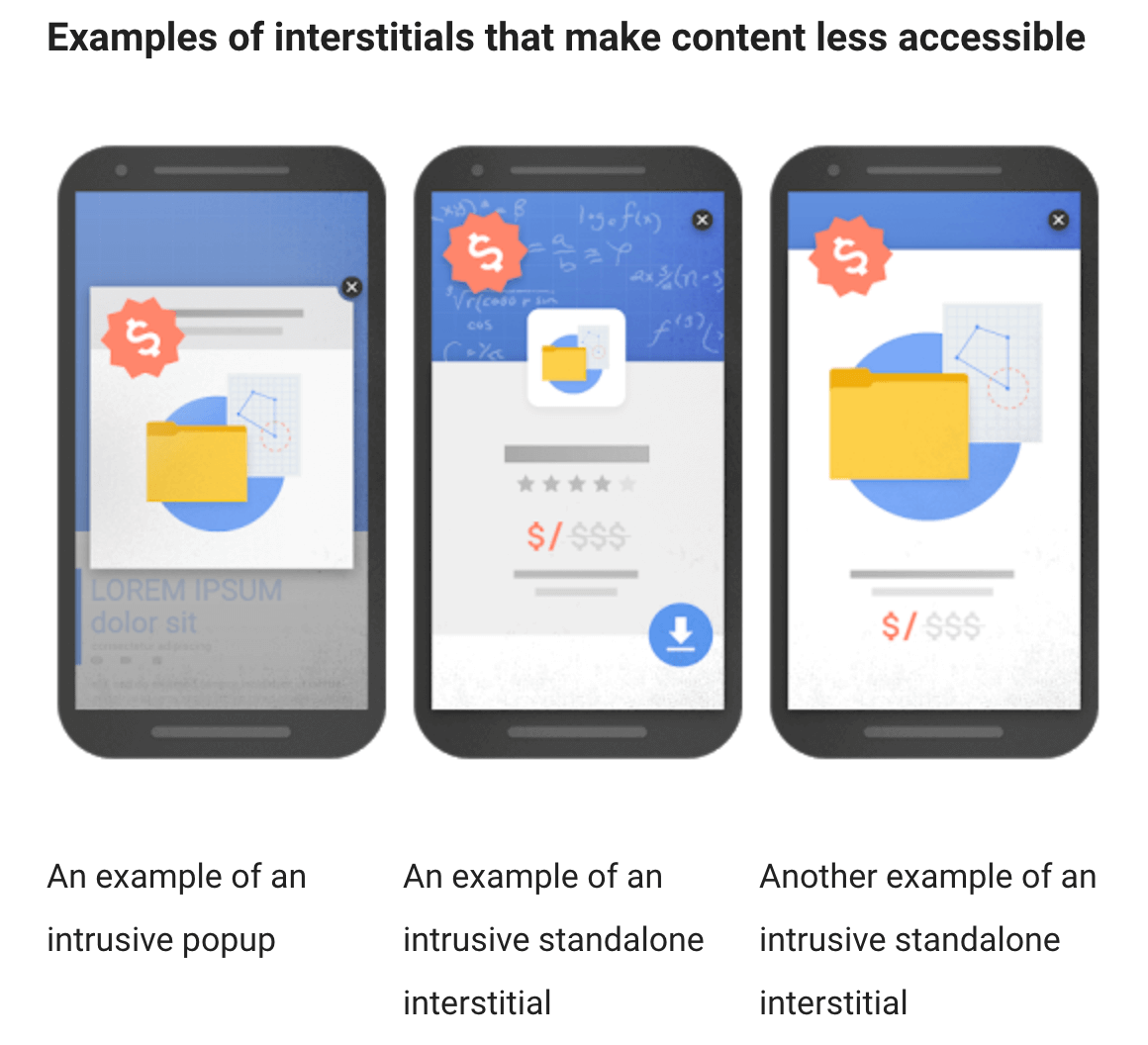
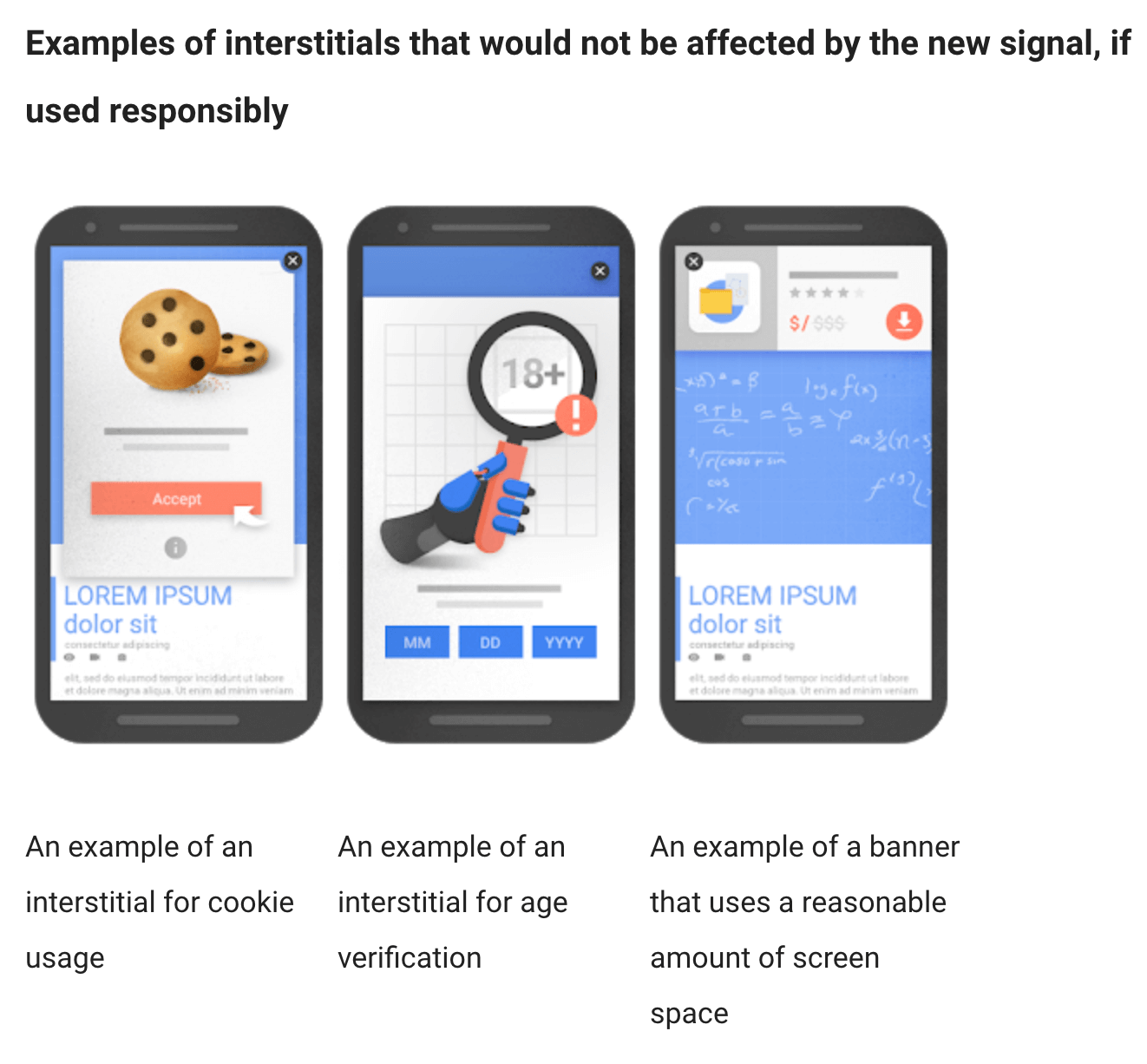
- And, the presence of interstitials (anything that interrupts a browsing session like pop-ups and advertisements).
The most notable addition to this new update is the integration of Essential Web Signals (or Core Web Vitals) with these pre-existing signals.
Another key update is that now content that is not formatted according to AMP standards can integrate with Google Top Stories, if it meets Google News content requirements.
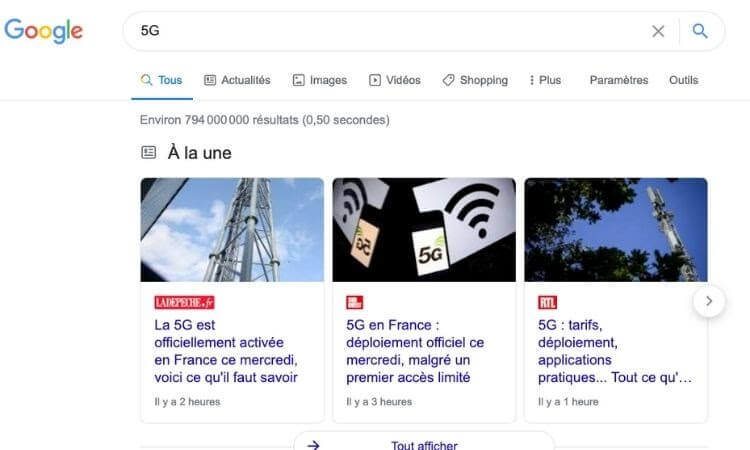
Top Stories de Google
Lastly, the update aims to reward outstanding UX pages with a visual distinction in the SERPs in the future.
While Google still prioritizes content over user experience, this could change in the future. Now, when evaluating similar content, UX will make all the difference.
What are Core Web Vitals?
Core Web Vitals or Essential Web Signals are tools for measuring the usability of a web page.
They take into account the page load performance (Largest Contentful Paint, or LCP), interactivity (First Input Delay, or FID), and visual stability (Cumulative Layout Shift, or CLS).
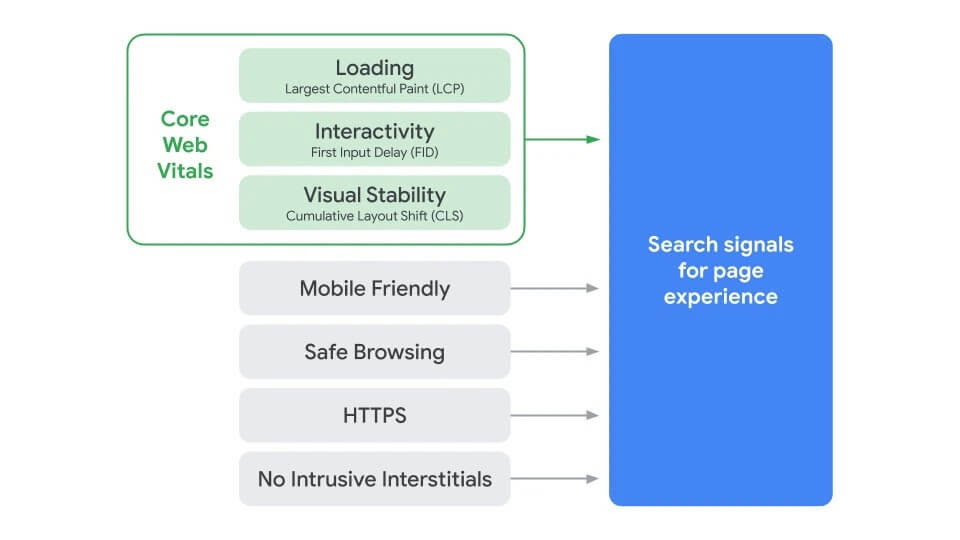
How the Core Web Vitals complement other UX signals - Source: Google
Let's take a closer look at what Essential Web Signals are:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) measures the perceived performance of a web page. It tracks the time it takes for the largest visible element on the page (textual or visual) to appear, which usually confirms for a user whether or not the page has what they’re looking for. A good LCP should be less than 2.5 seconds. If a page takes too long to load or prioritizes loading content not relevant to a user’s journey, odds are users will become frustrated and bounce from a page.
- First Input Delay (FID) measures the responsiveness of a page and how long it takes for a user to be able to interact with it. It measures the duration of time between a visitor’s first click on an element of the page (link, button, media, etc.) and the moment when the web browser is able to provide a response to this interaction. A good FID must not exceed 100 milliseconds.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) measures the visual stability of a page. Have you ever been reading an article when the text moves down the page for no apparent reason? Asynchronous page loading or third-party widgets can often cause these annoying on-page behaviors. The CLS is the sum of all unanticipated changes on a page and brands should aim for a CLS score below 0.1.

The Core Web Vitals Rating Scale - Source: Google
When is Google Page Experience Expected to Roll Out?
The Google Page Experience update is scheduled to launch in May 2021. If test results are conclusive, Google will also roll out non-AMP content and include a visual boost for pages with superior UX if the test results are conclusive. In order to maintain your site’s search results rankings, you need to offer an experience that meets or exceeds GPE's requirements.
How Can You Measure The Quality of Your User Experience?
There are many free and paid tools to assess the quality of the UX of a site or web page.
Here are a few ways you can get started evaluating your UX:
- Identify any pages on your site that need improvement or have site errors using Google Search Console’s Core Web Vitals report. The report is based on the Chrome UX Report (or CrUX) which is based on real-world usage data.
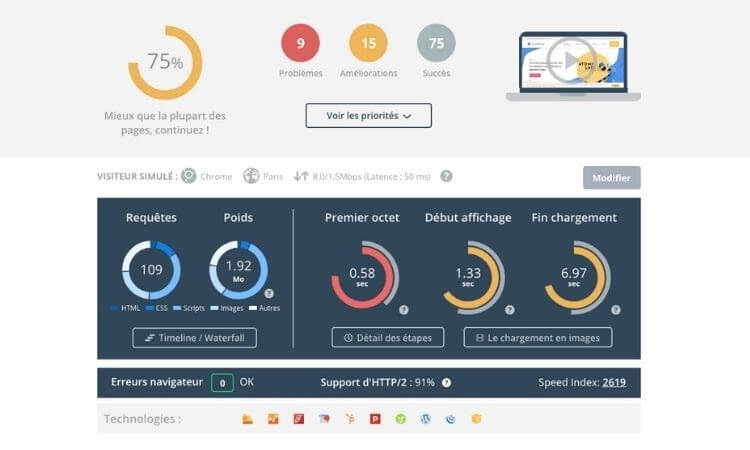
- Use PageSpeed Insights to analyze the content of a web page URL and identify opportunities to increase page speed.
- Finally, measure Core Web Vitals using Lighthouse and Chrome DevTools.
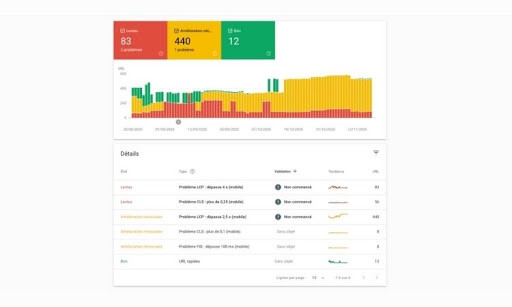
Google Search Console's Core Web Vitals Report